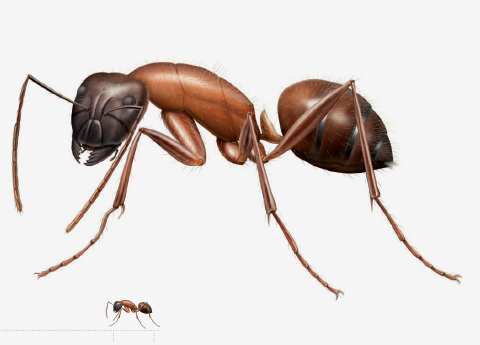
Carpenter Ant |
 |
Characteristics
|
Polymorphic workers, 1/4 to 1/2 in (7-13 mm) long |
Feeding PreferencesCarpenter ants feed primarily on insect honeydew, plant and fruit juices, and insects. Indoors, they feed on food debris, including sweets, eggs, meats, cakes, pet foods and grease. |
Nest Sites
Moderately sized mature colonies contain more than 3,000 workers with one queen per colony. (Colonies may contain satellite nests that consist of workers, larvae and pupae; together with the main colony, the total population may exceed 15,000.) Nests usually originate in moist, decayed wood and voids and may later expand into sound wood. Look for coarse sawdust piles (frass) that contain insect body parts and listen for the sound produced as workers chew to remove wood to enlarge the nest. Outside, nests are commonly found in dead or damaged portions of trees, rotting logs and stumps. |